Part 2 LeNet
约 1082 字大约 4 分钟
2025-08-04
LeNet 是最早发布的卷积神经网络之一,因其在计算机视觉任务中的高效性能而受到广泛关注。LeNet 在 1989 年被 Yann LeCun 提出并命名。
1 LeNet 结构
LeNet 由卷积编码器和全连接层稠密块两部分组成:
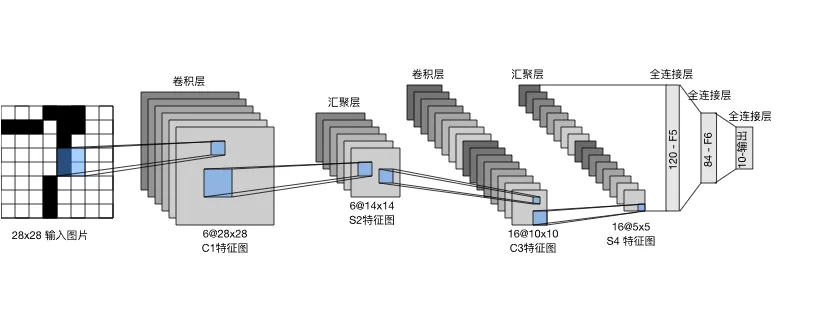
卷积编码器保罗两个卷积块,每个卷积块的基本单元是一个卷积层、一个 sigmoid 激活函数和一个平均池化层。每个卷积层使用 5×5 卷积核和一个 sigmoid 激活函数,将输入映射为多个通道的输出。第一卷积层有 6 个输出通道,第二卷积层有 16 个输出通道。每个 2×2 池化层将尺寸降低为原来的四分之一。
然后传递给全连接层稠密块。我们将这个四维输入转换成全连接层所期望的二维输入。这里的二维表示的第一个维度索引小批量中的样本,第二个维度给出每个样本的平面向量表示。LeNet 的稠密块有三个全连接层,分别有 120、84 和 10 个输出。因为我们在执行分类任务,所以输出层的 10 维对应于最后输出结果的数量。
2 LeNet 的 PyTorch 实现
使用 PyTorch 框架可以非常简单地实现 LeNet:
# 定义网络
net = nn.Sequential(
# 第一卷积块
nn.Conv2d(1, 6, kernel_size=5, padding=2), nn.Sigmoid(),
nn.AvgPool2d(kernel_size=2, stride=2),
# 第二卷积块
nn.Conv2d(6, 16, kernel_size=5), nn.Sigmoid(),
nn.AvgPool2d(kernel_size=2, stride=2),
# 全连接层稠密块
nn.Flatten(),
nn.Linear(16 * 5 * 5, 120), nn.Sigmoid(),
nn.Linear(120, 84), nn.Sigmoid(),
nn.Linear(84, 10))
# 初始化模型参数
def init_weights(m):
if type(m) == nn.Linear or type(m) == nn.Conv2d:
nn.init.xavier_uniform_(m.weight)
net.apply(init_weights)完整代码为:
import torch
from torch import nn
from torch.utils import data
import torchvision
from torchvision import transforms
def load_data_fashion_mnist(batch_size):
# 将 Fashion-MNIST 数据集转换为 Tensor
trans = [transforms.ToTensor()]
trans = transforms.Compose(trans)
minst_train = torchvision.datasets.FashionMNIST(
root="data/FashionMNIST", train=True, transform=trans, download=True
)
minst_test = torchvision.datasets.FashionMNIST(
root="data/FashionMNIST", train=False, transform=trans, download=True
)
train_iter = data.DataLoader(minst_train, batch_size, shuffle=True)
test_iter = data.DataLoader(minst_test, batch_size, shuffle=False)
return train_iter, test_iter
def accuracy(y_hat, y):
if len(y_hat.shape) > 1 and y_hat.shape[1] > 1:
y_hat = y_hat.argmax(axis=1)
cmp = y_hat.type(y.dtype) == y
return float(cmp.type(y.dtype).sum())
def evaluate_accuracy(net, data_iter, device):
if isinstance(net, torch.nn.Module):
net.eval()
metric = [0.0, 0.0] # [正确预测数, 总样本数]
with torch.no_grad():
for X, y in data_iter:
X, y = X.to(device), y.to(device)
y_hat = net(X)
metric[0] += accuracy(y_hat, y)
metric[1] += y.numel()
return metric[0] / metric[1]
def train(lr, num_epochs, train_iter, test_iter, device):
# 定义LeNet神经网络结构
net = nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(1, 6, kernel_size=5, padding=2),
nn.Sigmoid(),
nn.AvgPool2d(kernel_size=2, stride=2),
nn.Conv2d(6, 16, kernel_size=5),
nn.Sigmoid(),
nn.AvgPool2d(kernel_size=2, stride=2),
nn.Flatten(),
nn.Linear(16 * 5 * 5, 120),
nn.Sigmoid(),
nn.Linear(120, 84),
nn.Sigmoid(),
nn.Linear(84, 10),
)
# 初始化模型参数
def init_weights(m):
if type(m) == nn.Linear or type(m) == nn.Conv2d:
nn.init.xavier_uniform_(m.weight)
net.apply(init_weights)
# 将模型移动到指定设备
net.to(device)
# 定义损失函数:交叉熵损失
loss = nn.CrossEntropyLoss()
# 定义优化器:小批量随机梯度下降
optimizer = torch.optim.SGD(net.parameters(), lr=lr)
# 训练循环
num_batches = len(train_iter)
for epoch in range(num_epochs):
# 设置为训练模式
net.train()
# 用于统计本epoch的训练指标
train_loss = 0.0
train_acc = 0.0
for i, (X, y) in enumerate(train_iter):
X, y = X.to(device), y.to(device)
optimizer.zero_grad()
y_hat = net(X)
l = loss(y_hat, y)
l.backward()
optimizer.step()
# 累积损失和准确率
train_loss += l.item()
train_acc += accuracy(y_hat, y)
if (i + 1) % 100 == 0:
print(
f"Epoch [{epoch + 1}/{num_epochs}], Step [{i + 1}/{num_batches}], Loss: {l.item():.4f}"
)
# 计算本epoch的平均训练损失和准确率
train_loss /= num_batches
train_acc /= len(train_iter.dataset)
# 在测试集上评估模型
test_acc = evaluate_accuracy(net, test_iter, device)
# 打印epoch结果
print(f"Epoch [{epoch + 1}/{num_epochs}] 完成")
print(
f"训练损失: {train_loss:.4f}, 训练准确率: {train_acc:.4f}, 测试准确率: {test_acc:.4f}"
)
return net
def predict(net, test_iter, device, num_samples=10):
text_labels = [
"t-shirt",
"trouser",
"pullover",
"dress",
"coat",
"sandal",
"shirt",
"sneaker",
"bag",
"ankle boot",
]
net.eval()
# 获取一个batch的测试数据
X, y = next(iter(test_iter))
X, y = X.to(device), y.to(device)
with torch.no_grad():
y_hat = net(X)
predicted = y_hat.argmax(axis=1)
# 显示前num_samples个样本的预测结果
print(f"预测结果展示(前{num_samples}个样本):")
for i in range(min(num_samples, len(y))):
true_label = text_labels[y[i].item()]
pred_label = text_labels[predicted[i].item()]
print(
f"样本 {i+1}: 真实标签: {true_label}, 预测标签: {pred_label}, "
f"{'✓' if y[i] == predicted[i] else '✗'}"
)
# 计算整体准确率
overall_acc = evaluate_accuracy(net, test_iter, device)
print(f"\n测试集整体准确率: {overall_acc:.4f}")
if __name__ == "__main__":
# 超参数设置
batch_size = 256 # 批量大小
lr = 0.9 # 学习率
num_epochs = 10 # 训练轮数
device = torch.device("cuda" if torch.cuda.is_available() else "cpu")
# 加载数据
train_iter, test_iter = load_data_fashion_mnist(batch_size)
# 训练模型
net = train(lr, num_epochs, train_iter, test_iter, device)
# 进行预测
predict(net, test_iter, device)